
(10 mg/kg body weight every 2 wk) as a control (
n
= 4).
During the entire experimental duration, Enz (30 mg/kg
body weight every 24 h) was administered to all groups of
mice. Mouse tumor growthwas measuredweekly andmice
sacrificed after 4 wk. The results revealed that both
Malat1
-
siRNA and ASC-J9
1
significantly suppressed EnzR tumors
( Fig. 5 Cand D).
We also examined the AR-v7 and AR expression in vivo
through immunohistochemistry staining and results indi-
cated a significant reduction of AR-v7 expression in mice
treated with
Malat1
-siRNA and ASC-J9
1
while
Malat1
-
siRNA had little effect on AR
( Fig. 5 E).
4.
Discussion
Among several mechanisms involved in the development of
Enz resistance in CRPC, including induction of AR-v7
[4] ,ARF876L mutation
[16–18] ,and altered glucocorticoid
receptor signals
[19], the induction of AR-v7
[4]has the
strongest clinical data support derived from a clinical study
showing CRPC patients with detectable AR-v7 in CTCs had
poor responses to ADT-Enz
[4] .Furthermore, AR-v7 might
be linked to bone metastases in CRPC
[20] .These clinical
data point to the possible reason why ADT-Enz may always
fail after an initial clinical response. Therefore, it is
important to develop new approaches to suppress AR
function beyond antiandrogens since induced AR-v7 lacks
the ligand-binding domain and can be activated in the
castration condition
[21–24] .In this study, we found that
Malat1
expression and SF2 activity are upregulated in EnzR
C4-2 cells, which contributed to AR-v7 production and led
to Enz resistance
( Fig. 5F). Our finding is consistent with
previous work showing that SF2 could recognize and bind to
the intron between exon 3 and exon 4 of the AR transcript to
facilitate AR-v7 production
[25].
The linkage of Enz resistance to the induction of the
Malat1/
SF2
/
AR-v7 axis strongly suggests a new and better
therapy to further suppress CRPC during or after develop-
ment of Enz resistance, via targeting the
Malat1
, SF2,
and
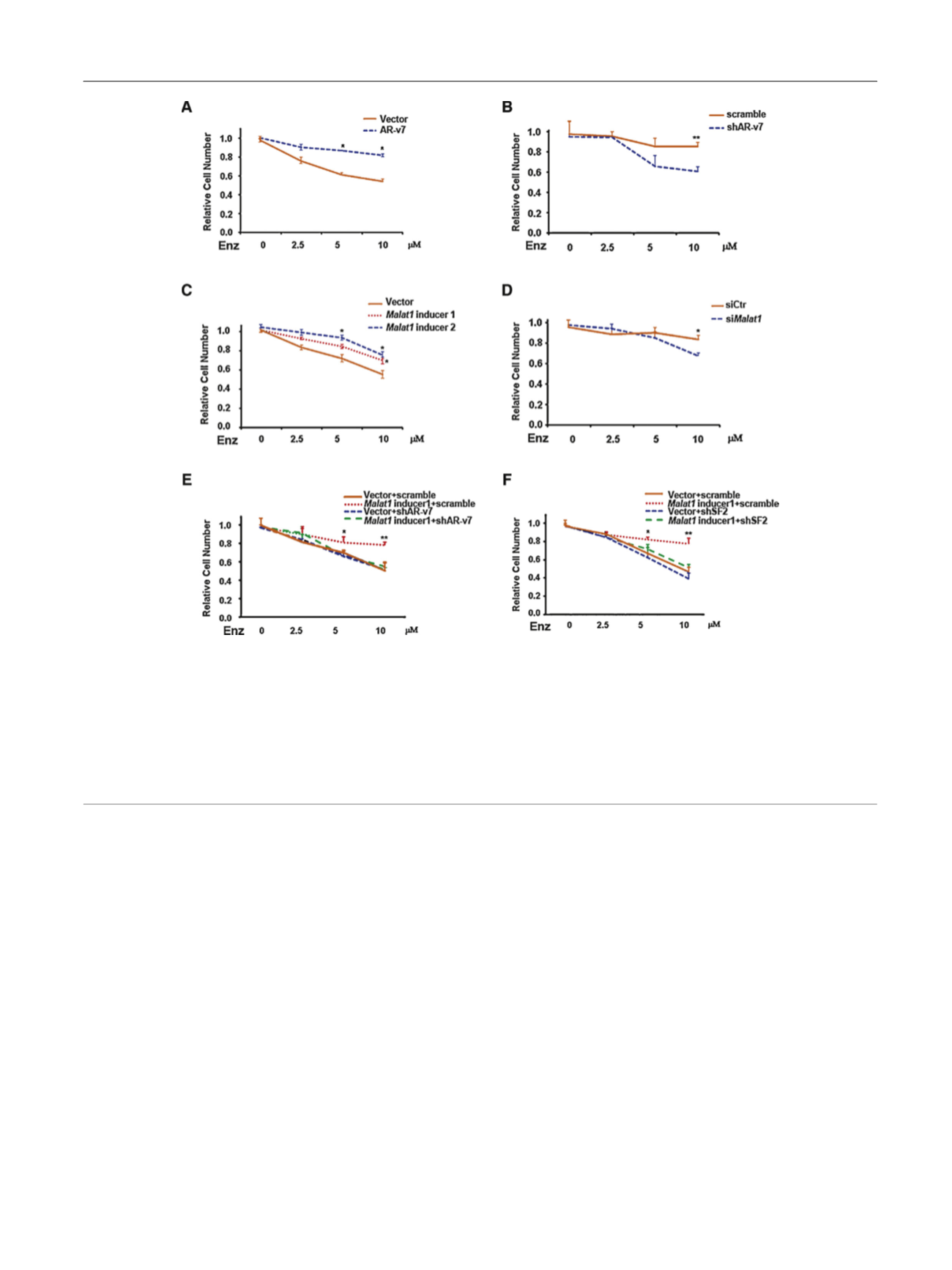
[(Fig._4)TD$FIG]
Fig. 4 – Androgen receptor splicing variant 7 (AR-v7) and
Malat1
confer enzalutamide (Enz)-resistance to prostate cancer cells. (A) AR-v7 stably
transfected C4-2 cell line displays Enz insensitivity compared with the control. Equal numbers of cells were seeded and subjected to various
concentrations of Enz. After 4 d, cell growth/viability was determined by MTT assay. (B) Knockdown of AR-v7 in EnzR cell line (R1) makes cells more
sensitive to Enz treatment. (C)
Malat1
-expressing cells show Enz insensitivity compared with control cells. Equal numbers of cells were seeded and
treated as indicated for MTT. (D) The deficiency of
Malat1
in EnzR cell line makes cells sensitive to Enz treatment. (E)
Malat1
-mediated Enz-resistance
can be reversed by short hairpin (sh)AR-v7. After two rounds of virus infection, equal numbers of cells were seeded and treated as indicated for MTT.
(F)
Malat1
-mediated Enz-resistance can be reversed by shRNA-serine/arginine rich splicing factor 1 (SF2) in cells seeded and treated as indicated for
MTT. For A-D the statistical analysis was made between
Malat1
-expressing cells and controls cells. For E-F ANOVA t test was performed among groups.
siCtr = si-control.
*
p
< 0.05
;
**
p
< 0.05.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 2 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 8 3 5 – 8 4 4
841
















