
reduced nocturnal diuresis of 0.59 ml/min and fewer
micturitions at night than for placebo (1.1 vs 1.7,
p
<
0.001; mean difference 0.59)
[12]. Twenty-four-hour
diuresis was unaffected. Another RCT looked at 60 men
receiving 0.1-mg desmopressin or placebo for 8 wk (LoE 2b)
[13] .Mean number of nocturia episodes reduced from 2.6 to
1.6 (vs placebo 2.5 to 2.3).
Antidiuretic therapy adverse effects are summarized in
Table 3 .The key adverse event of hyponatremia (
<
125 mmols/l), while rare, means that baseline sodium level
(
<
130 mmols/l) was a selection criterion in research
studies, and accordingly review of sodium levels is essential
during treatment. An RCT of 115 men older than 65 yr with
nocturia and nocturnal polyuria compared placebo with
nontitrated 0.1 mg desmopressin (LoE 1b)
[14], showing
decreased nocturnal urine output and number of nocturia
episodes (
p
<
0.01). The authors stated that long-term
desmopressin might induce hyponatremia gradually, but
specific data provided was limited.
Options for formulation and reduced dose level have
been further investigated. A 4-wk placebo-controlled
exploratory study described outcomes with low doses
(10–100
m
g) of desmopressin in 757 people (55% men; LoE
Table 3 – Adverse effects (AEs) during desmopressin treatment, in
studies where dose titration was undertaken
Study
Fu
et al
[43]Mattiasson
et al
[11]Van Kerrebroek
et al
[10]Patients exposed (
n
)
122
224
184
Total AE,
n
(%)
62 (50)
107 (48)
93 (51)
Serious AE
3 (3)
1 (
<
1)
3 (2)
Deaths
0
1 (
<
1
) aNR
AE related to
study medication
37 (39)
60 (27)
52 (28)
Headache
10 (8)
26 (12)
17 (9)
Nausea
5 (4)
10 (4)
NR
Hyponatremia
3 (3)
8 (4)
6 (3)
Abdominal pain
NR
NR
8 (4)
Dry mouth
NR
NR
5 (3)
Micturition frequency 0
NR
NR
Dizziness
6 (5)
NR
1 (1)
Fatigue
NR
NR
NR
Peripheral edema
NR
NR
NR
Hypertension
4 (3)
NR
3 (2)
Diarrhea
NR
9 (4)
NR
Insomnia
NR
NR
3 (2)
Diplopia
NR
NR
1 (
<
1)
Depression
NR
NR
1 (
<
1)
NR = not reported.
a
Unlikely to be study related (exacerbation of chronic lung disease).
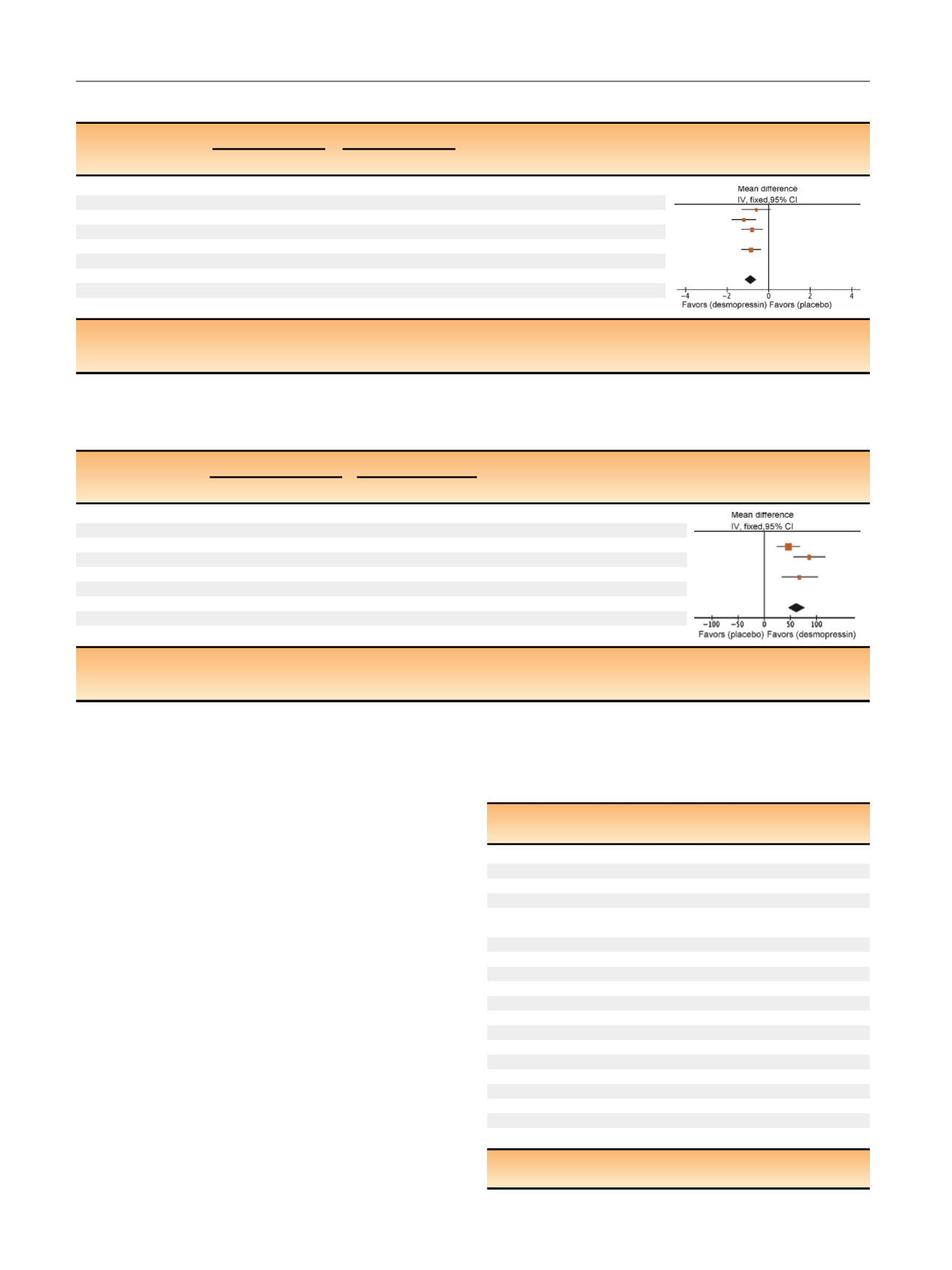
Table 1 – Effect of desmopressin (with dose titrated against response) on nocturnal voiding frequency
Desmopressin
Placebo
Mean difference
Study or subgroup Mean SD Total Mean SD Total Weight (%)
IV, fixed, 95% CI
Asplung 1999
–0.8 0.99 17 –0.2 1.1
17
15.4
–0.60 (-1.30, 0.1)]
Fu 2011
–1.5 1.28 39 –0.3 1.41 41
21.9
–1.20 (-1.79, –0.61)
Mattiasson 2002
–1.3 1.25 81 –0.5 1.75 62
28.8
–0.80 (-1.31, –0.29)
Rezakhanina 201
1 a–1
0
30 –0.2 0
30
Not estimable
Van Kerrebroeck
2007 –1.25 1.35 59 –0
.4 1.29 61
34.4
–0.85 (1.32, –0.38)
Wang 201
1 b–1.5 0
57 –0.8 0
58
Not estimable
Total (95% CI)
283
269
100
–0.87 (–1.15, –0.60)
Heterogeneity:
x
2
= 1.85, df = 3 (
p
= 0.60); I
2
= 0%
Test for overall effect: Z = 6.21 (
p
<
0.00001)
CI = confidence interval; df = difference; SD = standard deviation.
a
No standard deviation values.
b
No standard deviation values.
Table 2 – Effect of desmopressin (with dose titrated against response) on hours of undisturbed sleep
Desmopressin
Placebo
Mean difference
Study or subgroup Mean SD Total Mean SD Total Weight (%)
IV, fixed, 95% CI
Asplung 199
9 a102
0
17 18
0
17
Not estimable
Fu 2011
69.6 52.798
39 23.7 50.434 41
50.9 45.90 (23.25, 68.55)
Mattiasson 2002
110.4 102.71
81 24 84.483 62
27.7 86.40 (55.70, 117.10)
Rezakhanina 201
1 b120
0
30 30
0
30
Not estimable
Van Kerrebroeck
2007 108 106.5236
59 40 87.055 61
21.5 68.00 (33.13, 102.87)
Wang 201
1 b23
0
57 3
0
58
Not estimable
Total (95% CI)
283
269
100
61.85 (45.70, 78.00)
Heterogeneity:
x
2
= 4.48, df = 2 (
p
= 0.11); I
2
= 55%
Test for overall effect: Z = 7.51 (
p
<
0.00001)
CI = confidence interval; df = difference; SD = standard deviation.
a
No standard deviation values.
b
No standard deviation values.
E U R O P E A N U R O L O G Y 7 2 ( 2 0 1 7 ) 7 5 7 – 7 6 9
760
















